When More Testosterone Doesn’t Help Erectile Health – Part 1 of 2

The role of vascular health on male sexual function
“I’m injecting 150 mg of testosterone cypionate every week. I look muscular. I have lots of energy – so much I actually need to take sleeping pills to wind down at night. So why can’t I get a good erection? What is wrong with me?”
I counsel countless men* with stories like this.
Typically, these fellows come to see me after visiting a “Low T” clinic and trying various hormones and hormone precursors. From testosterone creams to shots, to HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin), to breast cancer drugs and beyond, hormone treatments do indeed help some men with erectile dysfunction – but fewer men than you might think.
Erectile dysfunction (ED, impotence) is a fairly common medical condition, characterized by the inability to achieve and maintain a penile erection firm enough for satisfying sexual intercourse.1
I often explain to my clients with ED that testosterone is just one piece of the puzzle. ED can also be caused by dysfunctions in the nervous system (including mental health), in the adrenal glands, in metabolic function, in B vitamin status, and in endothelial health (the inner lining of the blood vessels). The latter is also known as “endothelial ED,” a commonly overlooked aspect of sexual health – and the focus of this article.
40% of men above the age of 40 are now estimated to have some degree of ED.
Although ED is more common among older men,16 it’s becoming more common among younger men as well: 40% of men above the age of 40 are now estimated to have some degree of ED.13 While an estimated 152 million men worldwide had ED in 1995, that number is expected to swell (no pun intended) to over 320 million people by 2025.17,18 It’s no coincidence that heart disease is also on the rise: ED is often a warning sign of impending cardiovascular disease.
The mechanics of erection
Tumescence (penile erection) relies on proper blood flow. During the male sexual response, blood flow into the penis through the arteries increases, as blood flow out of the penile veins decreases.2,3 This process effectively traps blood in the penis, resulting in an erection.
The issue with ED tends to be with the first part of this process – the delivery of blood into the penis. The integrity of the circulatory system – the system of “highways” by which blood circulates throughout the body – is essential for male sexual performance and satisfaction.4
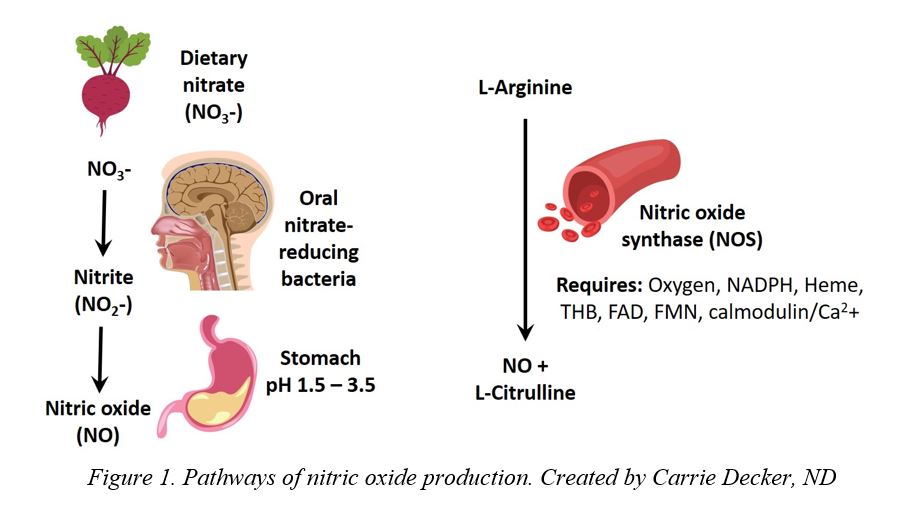
A key component of a healthy circulatory system lies in an important little gas called nitric oxide.
Nitric oxide gets the blood flowing
Nitric oxide (NO) is a tiny gas molecule found throughout the circulatory system, causing relaxation of the cavernous smooth muscle of the penis as well as vasodilation (widening) of the penile blood vessels. These combined effects allow more blood to pass into the penis, causing a firmer erection.5,6
One of the biggest culprits for compromising NO levels, however, is inflammation – specifically inflammation of the endothelium (lining of the blood vessels).7 Vascular inflammation and the NO deficiency it causes are also to blame for other cardiovascular problems, like angina (chest pain), heart attacks, and strokes.
Erectile dysfunction can be a warning sign of other impending diseases
Even in “well-endowed” fellows, the vessels of the penis are relatively small compared to the arteries in other parts of the body. This makes the penile blood vessels fragile and sensitive to injury. The penis is therefore often the first place in the body to manifest the signs and symptoms of vascular disease.
If left untreated, the vascular inflammation and NO dysfunction associated with endothelial ED may begin to spread to blood vessels in other parts of the body, causing a variety of serious heart problems like angina (chest pain), heart attack, and stroke.8 Men can develop ED before they develop even so much as an elevated blood pressure reading!9 That’s why ED is sometimes referred to as “painless penile angina.”10
ED is a warning sign of poor vascular function and impending cardiovascular disease.
A shocking 70% of men with coronary artery disease (CAD) in one study reported that they had ED long before they developed any symptoms of CAD.11 ED is a warning sign of poor vascular function and impending cardiovascular disease.6,11-13
ED and CAD share many of the same risk factors, including obesity, sedentary lifestyle, smoking, high homocysteine levels, diabetes, high blood pressure, dyslipidemia (high cholesterol), and metabolic syndrome. All of these risk factors are also associated with poor NO activity.6,13-15
Won’t more testosterone help?
Testosterone plays an important role in sexual function via several mechanisms, including the stimulation of NO release,23 but it’s unlikely to control endothelial ED on its own for very long.
For some people with endothelial ED, testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) may help, but not sufficiently unless the dosage is ramped up high – too high. Guys on too much testosterone often experience irritability, anxiety attacks, insomnia, or other symptoms of testosterone overdose. Because of the hormone’s influence on red blood cell (RBC) production, furthermore, guys on TRT are at high risk of life-threatening events like blood clots, chest pain, heart attacks, and strokes. They’re also prone to acne, “backne” (pimples on the back), a reddish complexion, and/or a puffy appearance – effects that make a guy look a bit like the Kool-Aid Man.
For many fellows with endothelial ED, even high doses of testosterone won’t cause strong erections.
For many fellows with endothelial ED, however, even high doses of testosterone won’t cause strong erections, which does not mean that the man’s penis is “broken!”
If you have endothelial ED, it’s important to understand how and why your blood vessels are dysfunctional. Yes, there are of course nutritional supplements you can take to enhance nitric oxide production, but they’re unlikely to give you the best outcomes unless you’re also taking care to stop the cause(s) of your vascular inflammation. This is where diet and lifestyle become non-negotiable.
In the next post, we take a look at some healthy strategies for improving endothelial health, increasing nitric oxide levels, and achieving strong erections.
Improving Erectile Health – Part 2 of 2

Nitric oxide support for sexual health
In Part 1 of this series, we looked at the physiology of a type of erectile dysfunction (ED) known as endothelial ED and explained the importance of blood vessel health on male sexual function. This week, we will explore some natural strategies, that have good scientific evidence for improving vascular (and erectile) integrity.
Although not all men with ED have endothelial ED, many of them do. Nevertheless, just about everyone can likely benefit from these suggestions:
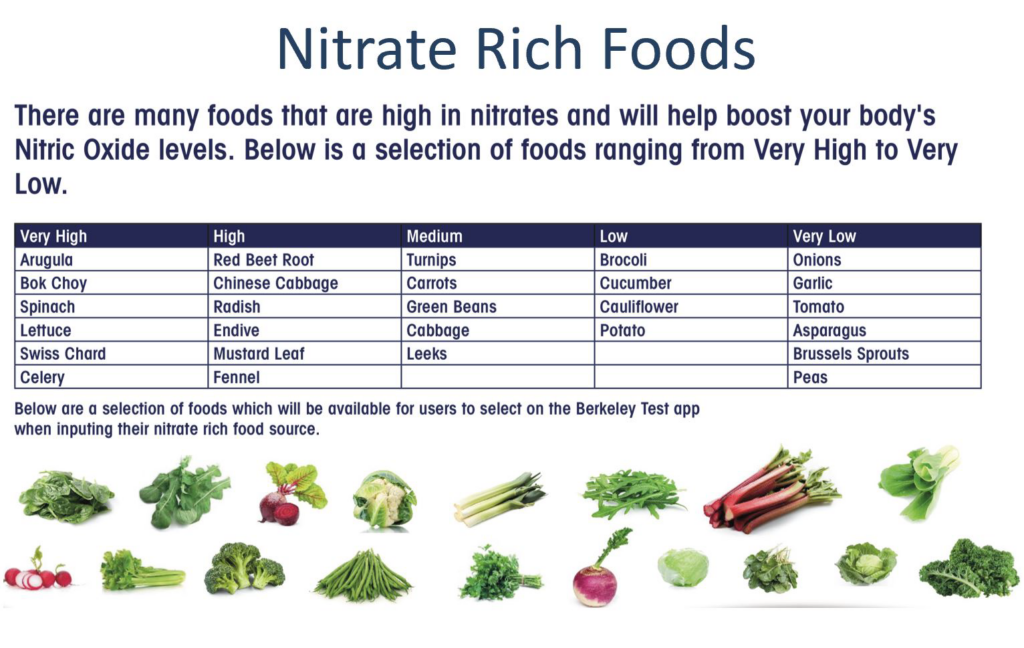
Eat vegetables – especially beets
Diets rich in vegetables have been shown to support overall heart health,[1],[2] lowering the risks of high blood pressure, heart attack, and stroke.[3],[4],[5] If you’re not eating vegetables – it’s never too late to start!
Make at least half of your plate at every meal greens (spinach, kale, chard, etc.) and/or brightly colored vegetables like purple cabbage, tomatoes, purple onions, carrots, and peppers. Beets (beetroot) are particularly effective in increasing nitric oxide (NO) levels, as they’re rich in nitrates, antioxidants, and phenolic compounds important for cardiovascular health.[6] Beets have been observed to increase NO levels and lower blood pressure readings in both men and women of various ages.[7],[8],[9]
Beets have been observed to increase NO levels and lower blood pressure readings in both men and women of various ages.
A powdered greens and/or powdered beetroot supplement (organic whenever possible!) can be a quick and easy way to consume more dietary nitrates.
Enjoy berries
Rich in flavonoids and antioxidants, blueberries, cherries, goji berries, and other berries are excellent for vascular health. Organic green tea, and dark chocolate can also fight oxidative stress, reverse endothelial dysfunction, and stave off cardiovascular diseases.[10]
Nix commercial mouthwash and stomach-reducing medicines
The brilliant human body converts the nutrients found in vegetables into NO. This conversion requires the presence of the right kind of bacteria in the mouth and enough stomach acid.[11]
Because most commercial mouthwashes kill both the good and the bad bacteria in the mouth, they may be contributing to endothelial ED and vascular diseases.
I also typically advise my clients to stay away from calcium carbonate tablets, omeprazole, and other medications that dampen stomach acid production.[12],[13],[14] (If you have acid reflux and think you need acid-reducing drugs, read this.)
L-arginine
The amino acid L-arginine is the raw material from which the body produces NO.[15] Low blood levels of L-arginine have unsurprisingly been correlated with poor NO production, and a significant percentage of ED patients have low levels of L-arginine and/or its precursor, L-citrulline.[16]
A significant percentage of ED patients have low levels of L-arginine and/or its precursor, L-citrulline.
L-arginine supplements may improve NO levels and erectile health – but with limited efficacy, as L-arginine only stays in the circulation for milliseconds at a time.[17] This may be why a review of L-arginine’s efficacy in the treatment of ED reports that a minimum dosage of 3 grams daily is necessary to achieve outcomes, and some studies have even dosed the amino acid at 5 grams.[18]
Thankfully, there is evidence that L-arginine may work significantly well when supplemented along with glutathione (GSH),[19] vitamin C,[20] pine bark extract,[21],[22] and/or L-arginine’s precursor, L-citrulline.
L-citrulline
L-citrulline is named for the watermelon, or Citrullus vulgaris, from which it is derived.[23] Unlike L-arginine, L-citrulline skips pre-systemic metabolism and effectively increases circulating NO levels.[24],[25] This might make L-citrulline a more advantageous nutritional supplement than L-arginine in the treatment of ED, hypertension, and related vascular conditions.[26],[27] It has also been shown to be an effective adjuvant to treatment with pharmaceutical PDE5 inhibitors (drugs like Sildenafil).[28]
What may be even more effective than L-arginine or L-citrulline monotherapy, however, is taking the two amino acids concurrently: Simultaneous oral supplementation of 1 gram of L-arginine and 1 gram of L-citrulline was shown to increase plasma L-arginine levels more than 2 g of either alone in a 2017 study.[29]
Caution: Because many viruses – including herpes simplex virus (HSV) – are dependent upon arginine for replication, L-arginine and L-citrulline supplements may be poorly tolerated by patients with frequent HSV outbreaks.[30]
French maritime pine bark extract
A standardized pine bark extract (SPBE) from the bark of the French maritime pine, Pinus pinaster – or Pycnogenol®, as it’s known in the U.S.A. by its patent name – has been shown to improve erectile function both as a standalone treatment and in combination with L-arginine.[31],[32]
SPBE has been observed to support the production and release of NO from the cells lining the blood vessels, improving forearm blood flow in humans in one study.[33]
SPBE has also been shown to improve erectile function, both as a standalone treatment and in combination with L-arginine.[34],[35] In one trial, for example, supplementation with SPBE (120 mg daily for three months) significantly reduced patients’ ED severity from moderate to mild.[36] The Pycnogenol group in this study was also observed to have increased plasma antioxidant activity and reduced total cholesterol and LDL-cholesterol levels as compared to the placebo group. These findings suggest that SPBE may not only treat ED, but also improve overall cardiovascular health.[37]
In another study of 40 males 25 to 45 years of age, a combination of L-arginine and Pycnogenol significantly outperformed Pycnogenol alone, helping 80% of men (and, after another month of the study, 92.5% of men) achieve a normal erection – as compared to only 5% of men who benefitted from Pycnogenol alone. Pycnogenol was given at a dose of 40 mg one to three times daily, with L-arginine at a dose of 1.7 g daily.[38]
A combination of L-arginine and Pycnogenol significantly outperformed Pycnogenol alone, helping 80% to 92.5% of men achieve a normal erection.
In a similar trial of 50 males, L-arginine (3 g per day) plus pycnogenol (80 mg per day day) restored normal erectile function after just one month of supplementation. Sperm quality improved in the men who took this combination and their testosterone levels increased significantly, thus suggesting enhanced fertility. The men also reported a doubling in their sexual intercourse frequency.[39]
Glutathione and other antioxidants
As the master antioxidant of the body, glutathione (GSH) strongly protects against the oxidative stress associated with endothelial dysfunction. GSH and other antioxidants may thus prevent oxidative stress, ameliorate vascular endothelial dysfunction, and stave off cardiovascular disease (among other chronic ailments).[40]
Supplementation with L-citrulline and GSH has also been shown to synergistically increase NO levels.[41]
DHEA
The steroid hormone precursor dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) enhances sex hormone production and positively effects NO levels, thus supporting endothelial health.[42]
A systematic review of 38 trials found that DHEA improves various aspects of sexual health.
A systematic review of 38 trials found that DHEA improves various aspects of sexual health in both males and females, including sexual interest, sexual frequency, lubrication, arousal, pain, and orgasm.[43] DHEA can also help with brain health.[44]
Avoid refined sugars and refined carbohydrates
Foods like breads, pastas, commercial pastries, candy bars, so-called “sports” drinks, sodas, most juices, cereals, crackers, and potato chips all increase blood glucose (sugar) levels and drive inflammation in the blood vessels. It’s no coincidence that men with diabetes and pre-diabetes are more likely to have ED than other guys.[45],[46]
Quit smoking and drinking
You know that smoking and drinking alcohol are harmful for your health, as does everybody else under the sun! These habits also create very high levels of inflammation and oxidative stress in the body, thus wreaking havoc on the circulatory system.[47],[48] ED may be a sign that it’s time to make some healthy lifestyle changes.
Mindfulness practice
NO helps with more than just the dilation of blood vessels: it also supports immune function, balances the nervous system,[49] and protects against various types of dementia.[50] NO helps us feel more relaxed, in turn supporting further NO production.[51] In fact, experienced meditators were found to have higher levels of NO precursors in their blood than non-meditators, in one study.[52]
Move your body
A sedentary lifestyle is a significant risk factor for ED and other cardiovascular diseases. Exercise is the number one lifestyle factor most strongly correlated with erectile health.[53]
Exercise is the number one lifestyle factor most strongly correlated with erectile health.
A review of ten studies found that moderate to vigorous aerobic exercise (four times weekly for six months) improved erectile function in men with ED caused by sedentary lifestyle, obesity, high blood pressure, cardiovascular disease, and/or metabolic syndrome.[54]
Physical activity is an effective way to prevent – and likely treat – ED because it increases NO levels, improves vascular function,[55] and increases testosterone.[56] Considering that exercise helps with a wide array of other health conditions, physical activity should be a part of just about every person’s day. (Too busy to move? Read our tips for fitting exercise into your day.)
Conclusion
During male sexual arousal, nitric oxide (NO) delivers blood to the penis, resulting in erection. Erectile dysfunction may therefore sometimes be a symptom of poor circulatory health, high vascular inflammation, and/or low nitric oxide (NO) levels – all of which can predispose a man to more serious problems like high blood pressure, angina, heart attack, and stroke. ED can therefore serve as an important warning signal of bigger problems to come.
Thankfully, some simple, natural strategies can make all the difference.
Note: The words “man,” “guy,” “fellow,” and “male” as used within this article refer specifically to individuals who were born with XY chromosomes and a penis. I acknowledge and honor that not all men are born with this anatomy, and that not all people born male identify with that gender.